
- #Get command line for app in mac install#
- #Get command line for app in mac software#
- #Get command line for app in mac free#
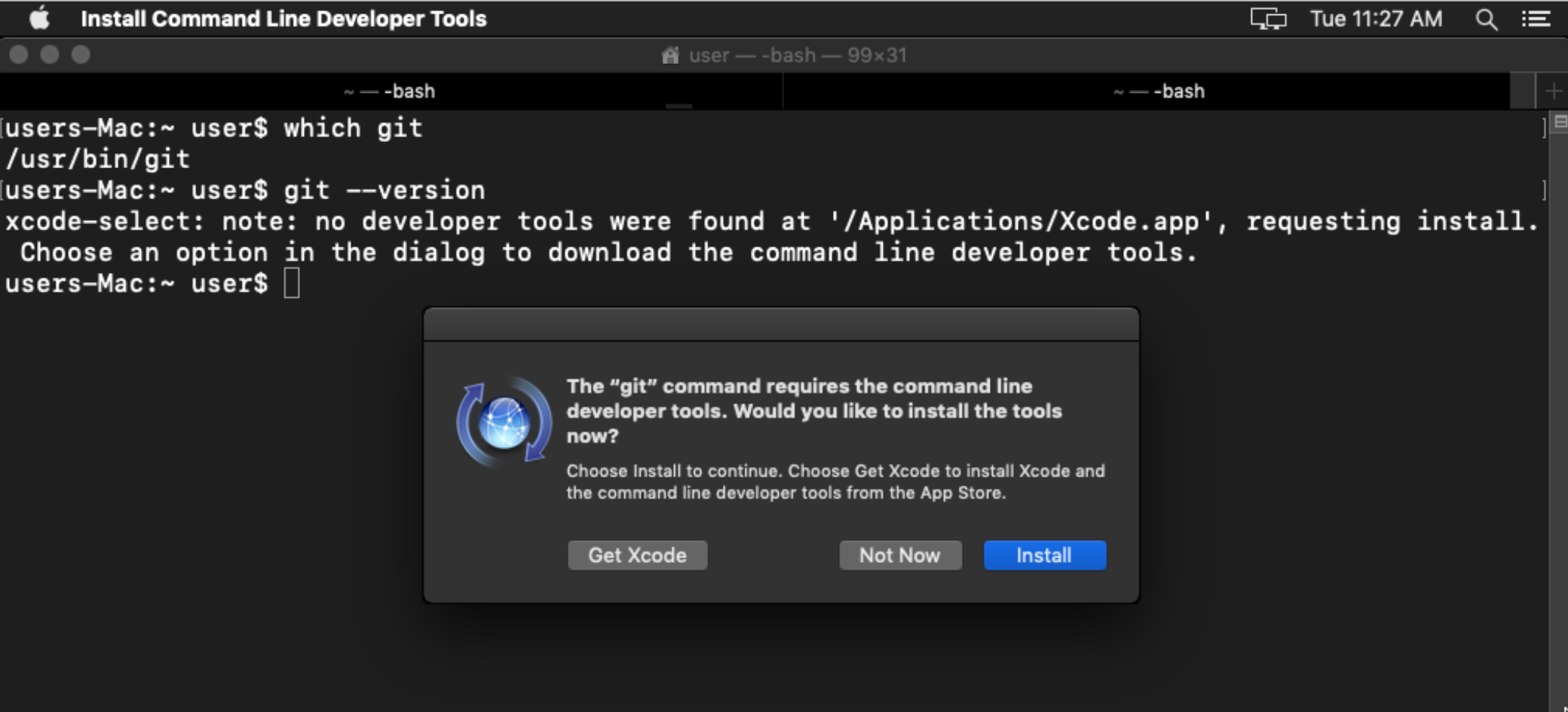
Xcode is an integrated development environment (IDE) that is comprised of software development tools for macOS. Step 2 - Installing Xcode’s Command Line Tools
#Get command line for app in mac install#
Now that you have the Terminal running, let’s install some additional tools that Homebrew needs. The command line interface on macOS is very similar, and the concepts in that tutorial are directly applicable. To get more comfortable using the command line, take a look at An Introduction to the Linux Terminal.
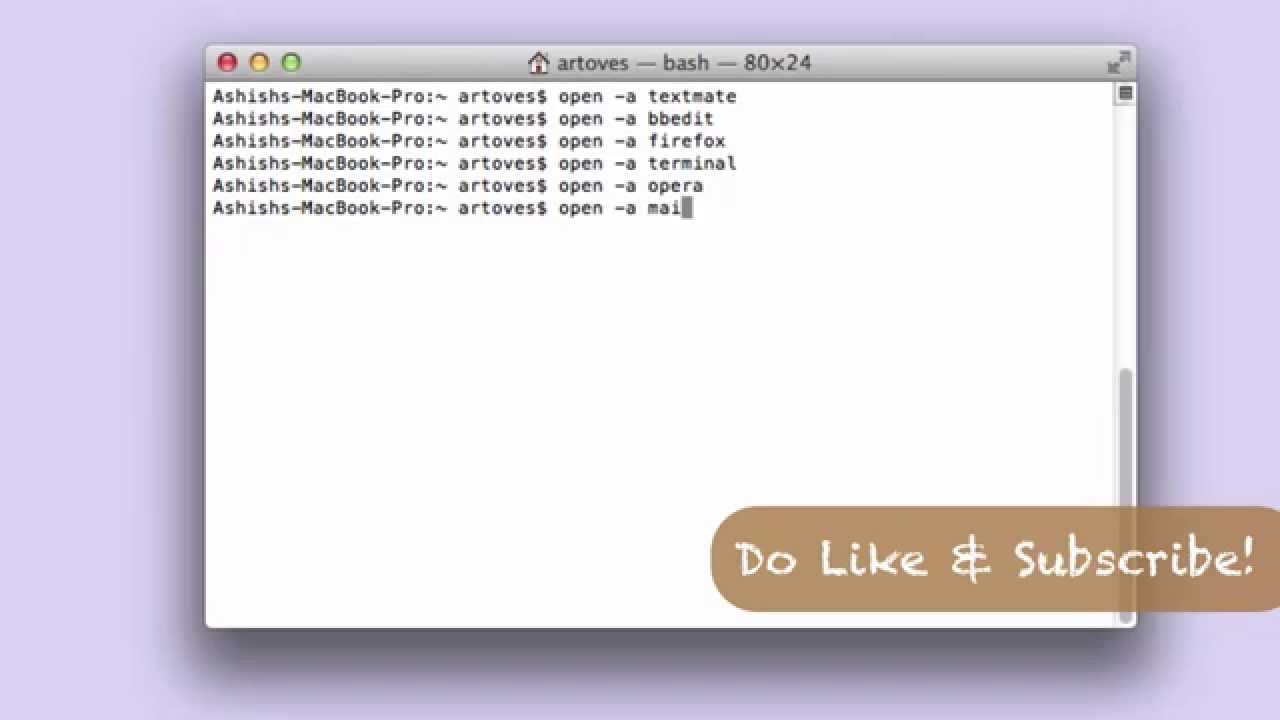
Alternatively, you can use Spotlight by holding down the COMMAND key and pressing SPACE to find Terminal by typing it out in the box that appears. From here, double-click the Terminal application to open it up. Like any other application, you can find it by going into Finder, navigating to the Applications folder, and then into the Utilities folder. To access the command line interface on your Mac, you’ll use the Terminal application provided by macOS. While older versions of macOS may work, they are not officially supported. You will need a macOS computer running Catalina or higher with administrative access and an internet connection. You’ll install system tools and desktop applications from the command line interface. In this tutorial you’ll install and use Homebrew on your Mac. You’ll use Homebrew to install developer tools like Python, Ruby, Node.js, and more.
#Get command line for app in mac free#
Homebrew is a package manager for macOS which lets you install free and open-source software using your terminal. Package managers keep the software they install in a central location and can maintain all software packages on the system in formats that are commonly used. A package manager is a collection of software tools that work to automate software installations, configurations, and upgrades. While the command line interface on macOS has a lot of the functionality you’d find in Linux and other Unix systems, it does not ship with a package manager. The command line, also known as a shell, lets you automate many tasks you do on your computer daily, and is an essential tool for software developers. Instead of clicking buttons with your mouse, you’ll type commands as text and receive text-based feedback. You may click the "Copy" button to copy the command line to the clipboard.The command line interface is a non-graphical way to interact with your computer.Click on the window you would like to know the command of.Run the file by double-clicking and selecting "Run".Save the above script into a file and make it executable.If thenĮcho -e "The package 'wmctrl' must to be installed before to run $(basename $0).\nUse 'sudo apt-get install wmctrl' command to install it." IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE #THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. #The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software. #Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:

#Licensed under the standard MIT license: #appcmd - script which use the application window title to find out the right command which opens the respective application from terminal I just made the following script which use the application window title to find out the right command which opens the respective application from terminal (I named it appcmd): #!/bin/bash


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
